Scope/Description
- This article describes the process of mounting an NFS share to a linux client and to mount on reboot.
Prerequisites
- NFS Share Configured on a Server, see here
- nfs-common installed on client(detailed below)
Steps
Install NFS Package
Ubuntu
- Use the following command to install nfs-common, this is required to mount NFS share to the client system.
apt install nfs-common
Rocky
- The following command will install the required nfs packages to mount an NFS share to a client system.
dnf install nfs-utils
Mount NFS Share
- To mount an NFS share, first create a directory to mount it to.
mkdir /mnt/(mount_point)
![]()
- Now use this command to mount it to the share. Edit the fields for your specific case, i.e. Server IP, Pool Name, and Share Name. See example below.
mount -t nfs {ServerIP}:/(pool_name)/(nfs_share_name) /mnt/(mount_point)
![]()
Add Mount on Reboot
- To allow the share to mount on reboot, you will need to edit the fstab. You can use your preferred text editor, here I use vim.
vim /etc/fstab
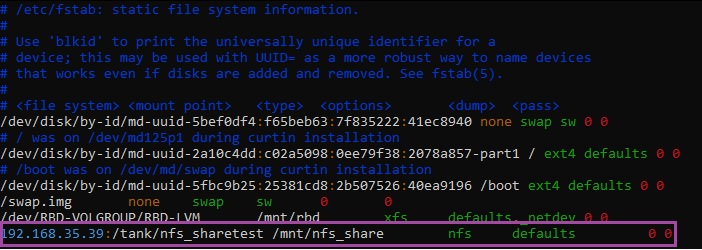
- Add the mount point in the format see below.
{ServerIP}:/(pool_name)/(share_name) /mnt/(mount_point) nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
Verification
Verify Share Mounted
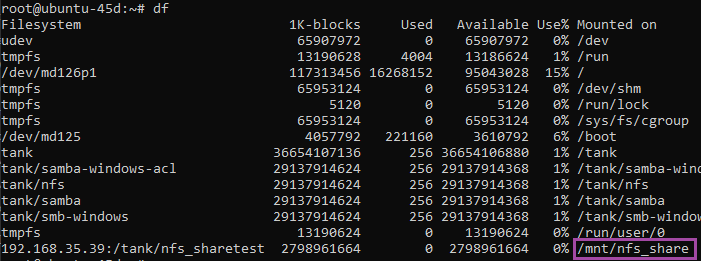
- To ensure the share has mounted, you can run the command df.
Verify Mount on Reboot
- To ensure the share will mount on reboot after editing the /etc/fstab, unmount the share.
umount /mnt/nfs_share
- Remount the share using the following command, this command will mount all shares in the /etc/fstab file.
mount -a
- Run df again to ensure the share was mounted.
df
Troubleshooting
- If the share will not mount, ensure the directory is correctly configured on the server side, and the nfs directory has permissions 770 set.
- If the server will not mount the share on reboot, the /etc/fstab is very particular, ensure the correct syntax.
Views: 1505