Scope/Description
- This article will cover creating and managing SMB shares in Houston UI.
Prerequisites
- Access to Houston UI
- Cockpit File Sharing Module and Packages Installed
- SMB Packages Installed
- SMB Services Running and Enabled
- SMB Ports Open on Firewall (133/tcp, 445/tcp and 137/udp, 138/udp)
Steps
Accessing the File Sharing Tab
- In Houston UI, navigate to the File Sharing tab.
- Once here, we can begin configuring our SMB Shares

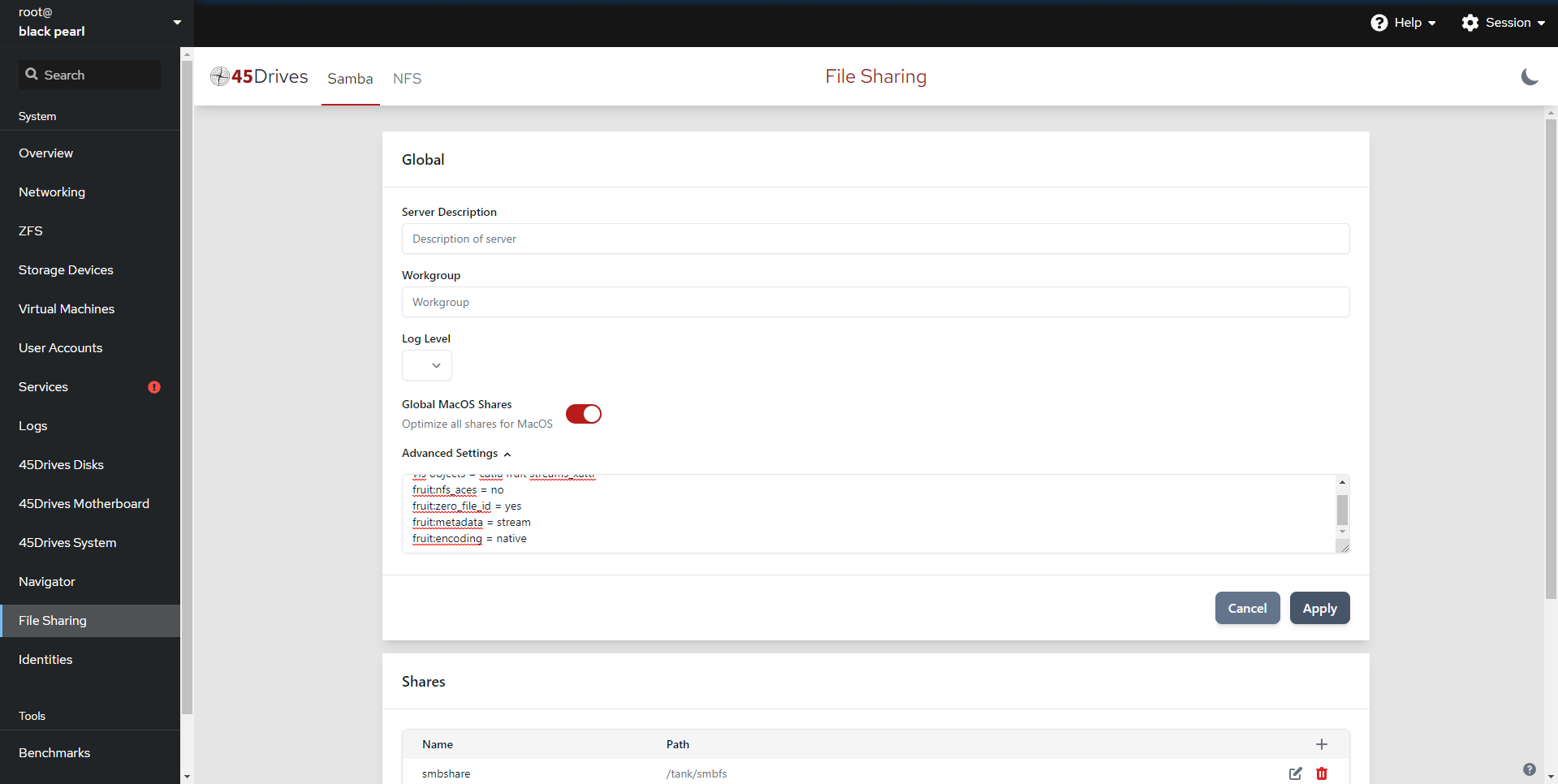
Adding options to the smb.conf global section
- First, we can add any options to the Global SMB configuration.
- Here we can change the Server Description, the Workgroup, Log Level, and add any additional parameters to the SMB configuration in the Advanced Settings box by clicking the down arrow. For example, here we’ve added a few parameters to help with MacOS performance on an SMB share.
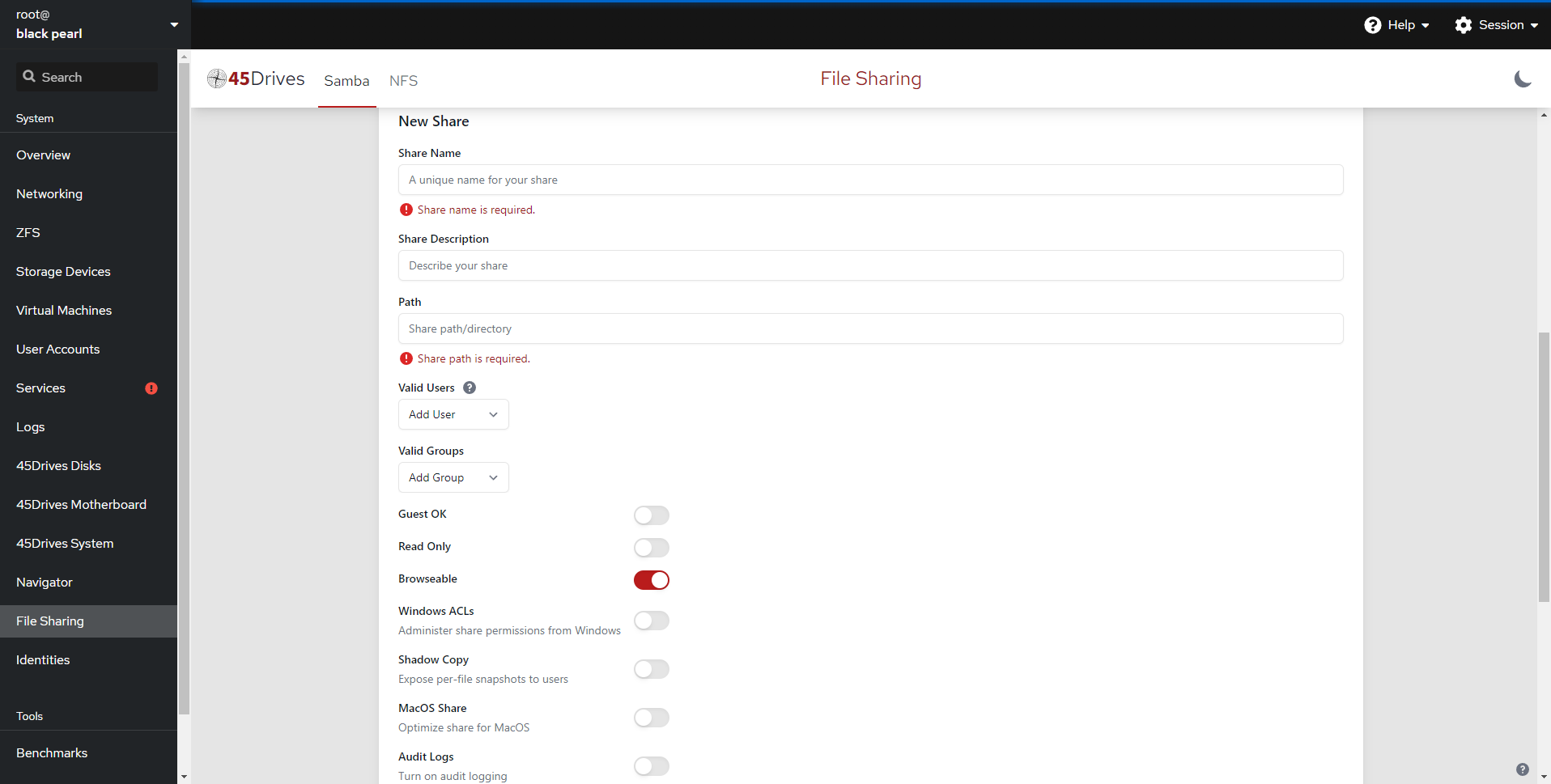
Creating an SMB share
- Next we can create an SMB share, we can scroll down to Shares and select the Plus button to begin.
- Here we can set the SMB Share Name, a Description, the Path to be shared out (you can now create the path here instead of ZFS), if we are domain joined we can select to use Windows ACLs. We can specify any Valid Users and Valid Groups, allow Guest Access, make the SMB share Read Only, make it Browsable, and enable Windows ACLs, as well as some other options.
Adding options to the SMB share
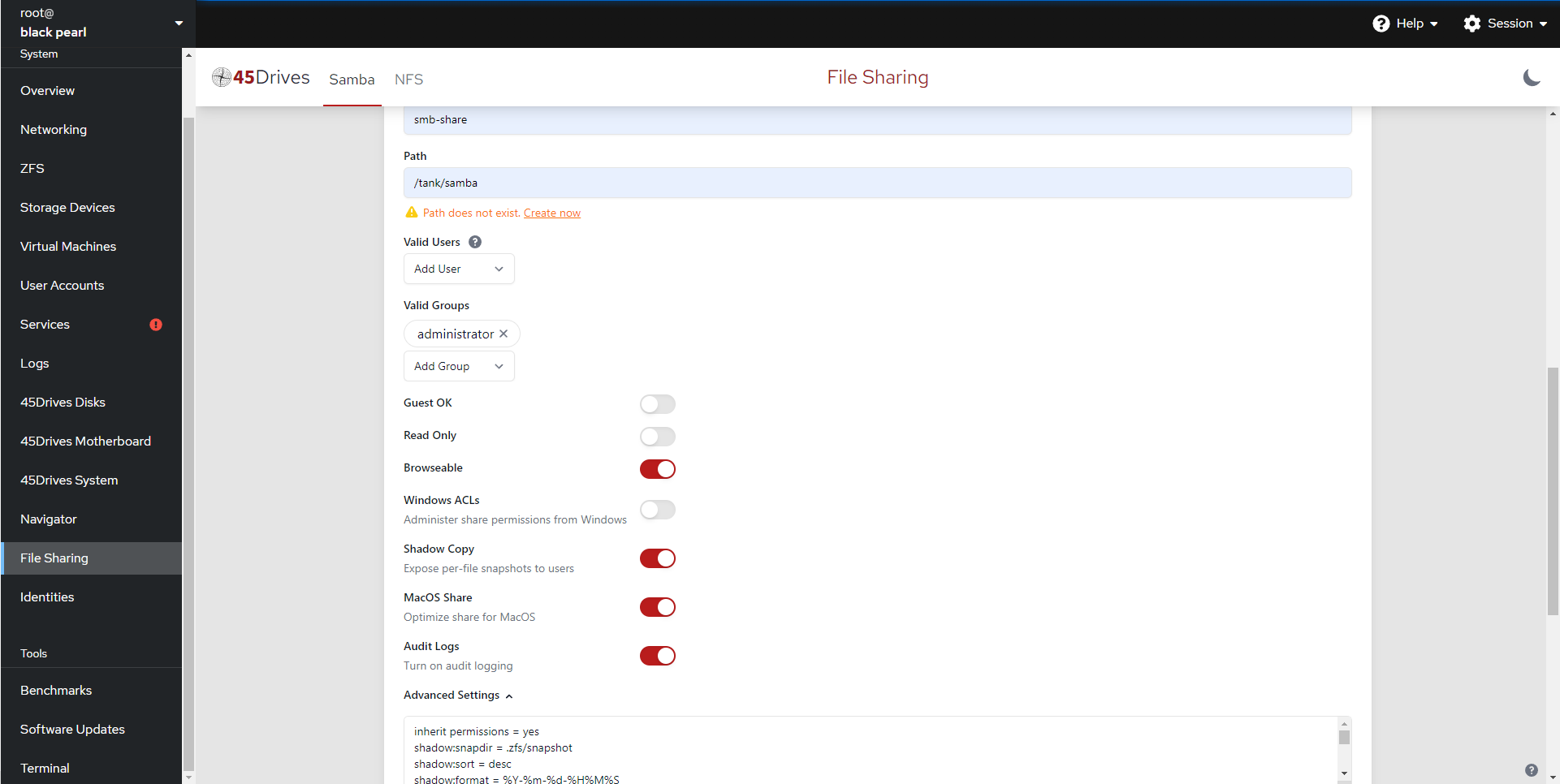
- We can also add any additional options in the Advanced Settings box via the drop down arrow.
- In the Advanced Settings box, we entered “inherit permissions = yes” ourselves.
- There is a few preselected options we can enter into the Advanced Settings box by selecting one of the buttons below: Shadow Copy, MacOS Share, Audit Logs.
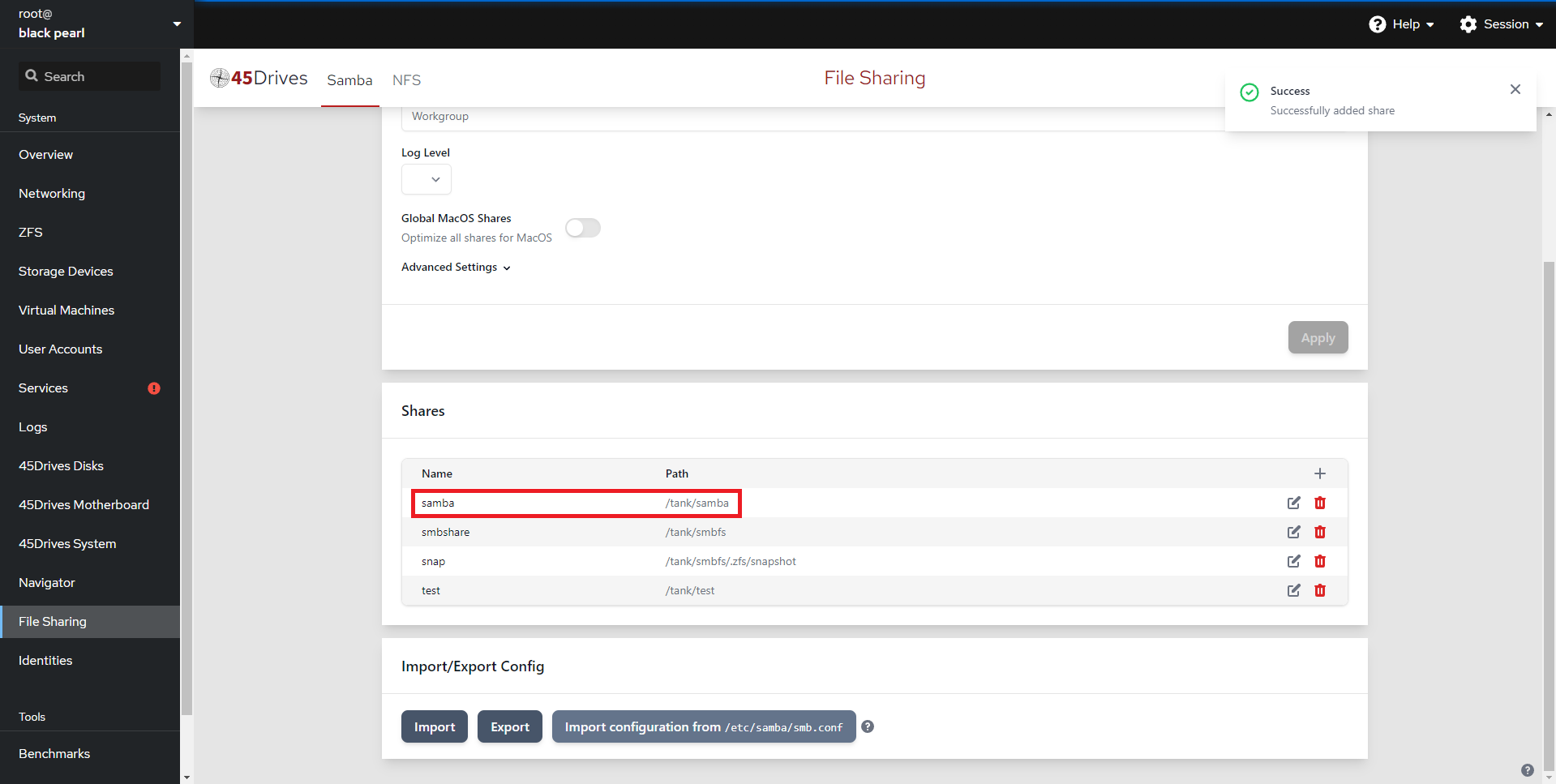
- Here we can see we’ve created a share called “samba” with a description of “smb-share“. It is pathed to our ZFS dataset at “/tank/samba“. We have added the “administrator” to Valid Groups, and left the share Browsable.
If you want to use this share for macOS Time Machine backups, then you will need to add these options:
vfs objects = fruit streams_xattr
fruit:time machine = yes
- Here we can see our SMB share is created.
 If you’d like to see an example of some basic SMB shares, as well as setting up local SMB users and groups, please see the Further Reading section below
If you’d like to see an example of some basic SMB shares, as well as setting up local SMB users and groups, please see the Further Reading section below
Verification
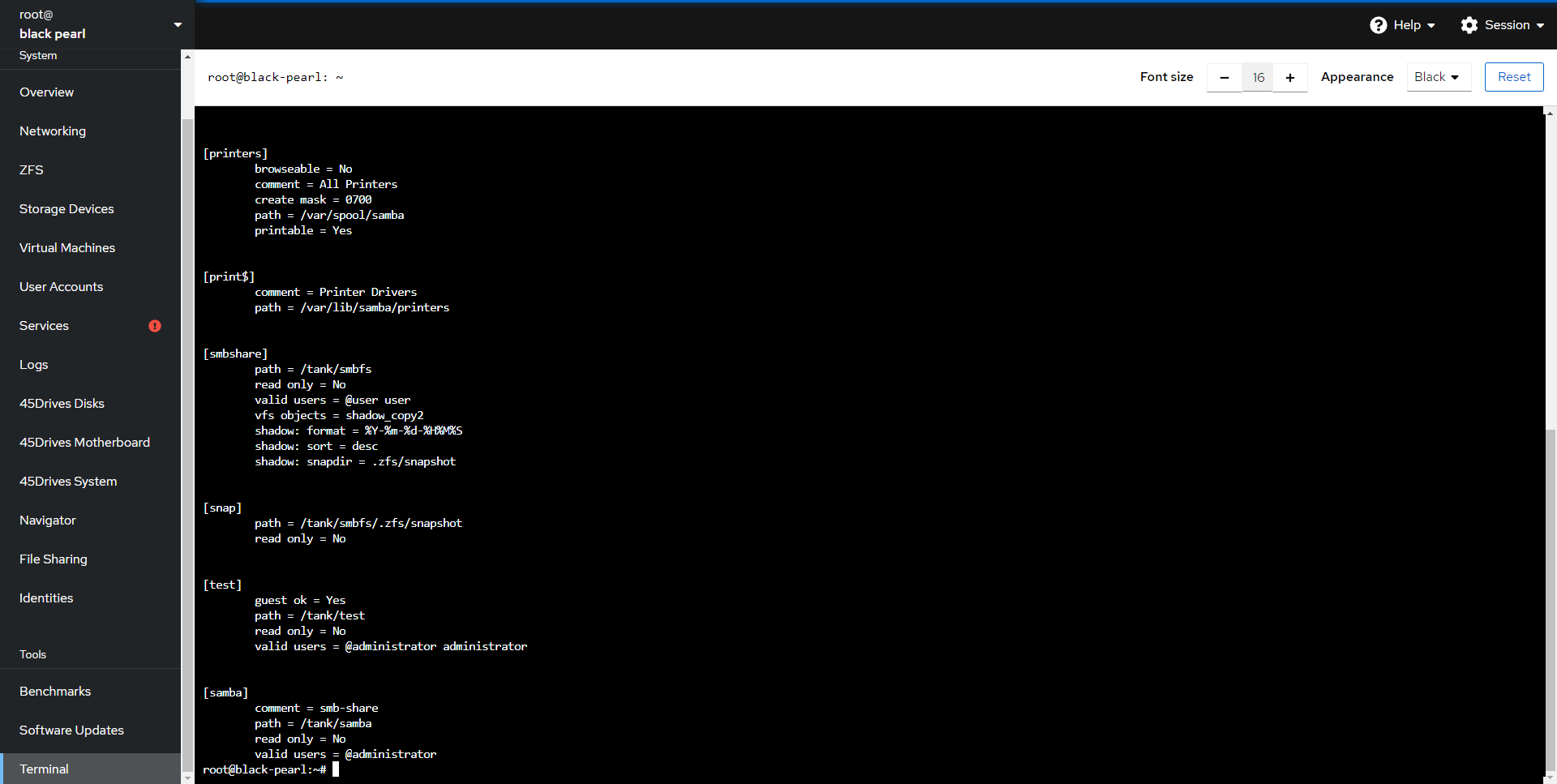
- If you were to run “testparm -s” on the command line you will see your samba share has been added and configured properly in its own section.
Troubleshooting
- Ensure you have configured the Firewall correctly.
- Ensure you have the smb/smbd service running and enabled.
- Ensure you have configured the correct permissions on the directory that is being shared out. Typically when using POSIX ACLs we would set the permissions to 770 and the owner user/owner group to the user/group that should own the SMB share.
- Ensure the user connecting has an SMB password set.
- Ensure the user connecting is part of the group that owns the SMB share.
- Ensure SeLinux is set to permissive if Rocky Linux.
- Ensure the value for 127.0.1.1 matches the systems hostname if Ubuntu 20.04.
Further Reading
Views: 10863