Table of Contents
Scope/Description
- This article will cover installing Houston UI for CentOS 7.
Prerequisites
- CentOS 7 installed
Steps
- First, we’ll update to the latest packages
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum update -y
- Reboot after the update if there is a new kernel.
- Install epel-release.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum install epel-release -y
- Next, we’ll install the ZFS packages.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum install http://download.zfsonlinux.org/epel/zfs-release.el7_9.noarch.rpm
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum install -y kernel-devel zfs
[root@centos7-45d ~]# echo zfs > /etc/modules-load.d/zfs.conf
[root@centos7-45d ~]# modprobe zfs
- Reboot to ensure ZFS loads correctly on startup.
- Set SELinux to permissive.
[root@centos7-45 ~]# setenforce 0
- To keep the permissive setting after reboot.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# sed -i 's/^\(SELINUX=\).*$/\1permissive/' /etc/selinux/config
- Pull down the 45drives Repository.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# curl -sSL https://repo.45drives.com/setup | sudo bash
- Install the following packages.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum install -y cockpit cockpit-pcp 45drives-tools
- Enable the cockpit socket.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
- Add a firewall rule for cockpit.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9090/tcp; firewall-cmd --reload
- Install Houston UI modules.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# yum install -y cockpit-zfs-manager cockpit-45drives-hardware cockpit-file-sharing cockpit-navigator cockpit-benchmark cockpit-storaged
- Now, run dmap to update the drive aliasing,. It should clearly display the installed drives in each slot and their identifiers using lsdev.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# dmap
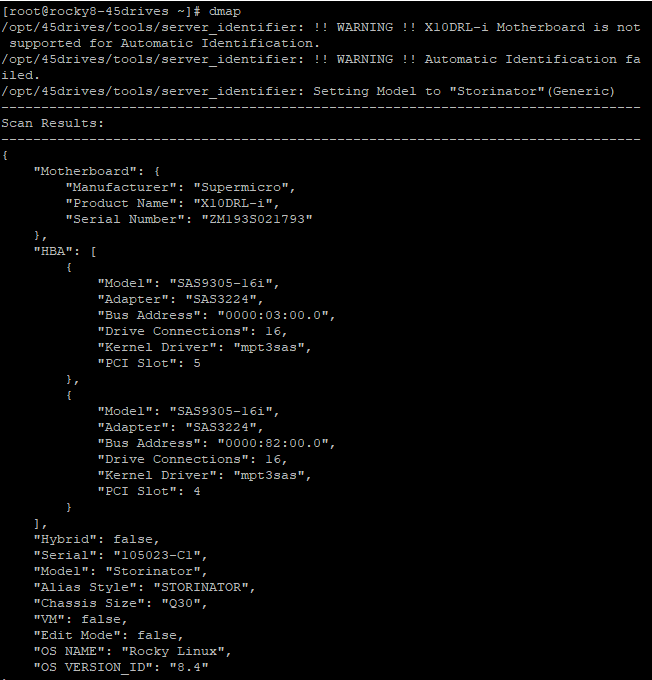
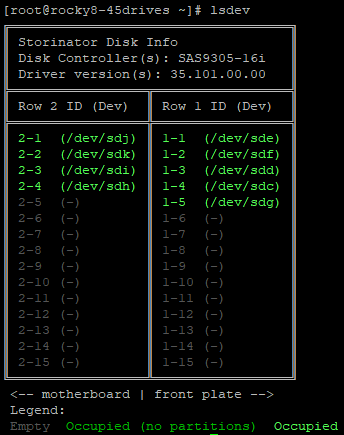
- Now you can run “lsdev”.
[root@centos7-45d ~]# lsdev
Verification
- Houston should now be installed and reachable at serverip:9090 in any web browser.
Troubleshooting
- If Houston is inaccessible, ensure cockpit is running, then restart the service.
systemctl status cockpit systemctl restart cockpit
Views: 1315