Scope/Description
- This article provides the steps to join an Ubuntu 22.04 system to an Active Directory (AD) domain using a single Samba server configuration, leveraging the Samba-Ansible playbook and the Winbind daemon for user and group resolution.
- Please note that this is compatible with Ubuntu 20.04 version as well.
Description
- This knowledge base article details the process of using the samba-ansible package, which provides pre-configured Ansible playbooks, to automate the domain join process.
Prerequisites
- An Ubuntu 22.04 server installation.
- The server must have its network settings configured (DNS pointing to the AD Domain Controllers).
- SSH access to the Ubuntu server.
- Sufficient permissions to install packages using sudo.
- A valid Active Directory user account with permissions to join computers to the domain (e.g., user@REALM).
- The Samba server must be configured as a domain member.
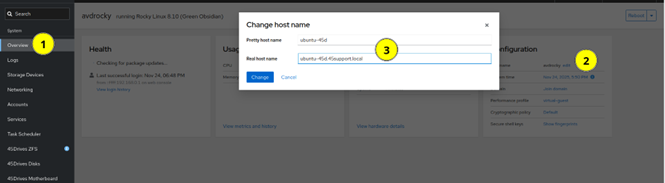
Configuring Hostname and DNS
- Set hostname of the system to include domain name if not set already, this is done in the Overview tab of the Houston UI.
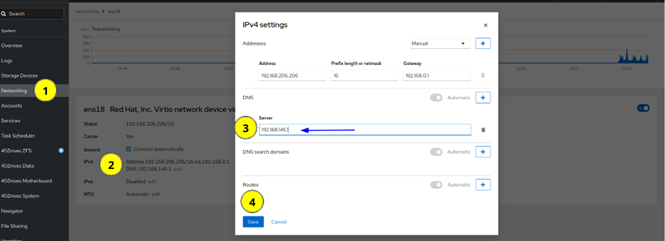
- Set DNS server to the IP of the Domain Controller if not done already. This is done in the network tab of the Houston UI
Steps
Step 1: Install Samba-Ansible and Kerberos User Packages
Install the necessary packages, which include the Samba-Ansible playbooks and the Kerberos user utilities for authentication.
Run the following command to install the required packages:
sudo apt install samba-ansible krb5-user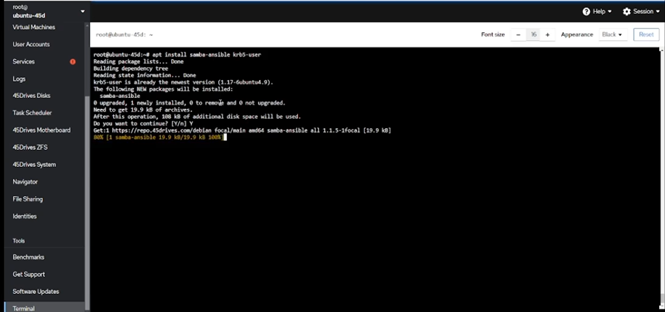
The Ansible playbooks are installed in the /usr/share/samba-ansible directory. Navigate to this directory:
cd /usr/share/samba-ansible
Create an Ansible inventory file named hosts and populate it with a group called smbs containing the local server’s hostname:
printf "[smbs]\n$(hostname -s)\n" > hosts
Create and populate the smbs.yml group variables file from the sample:
cp group_vars/smbs.yml.sample group_vars/smbs.yml cd group_vars
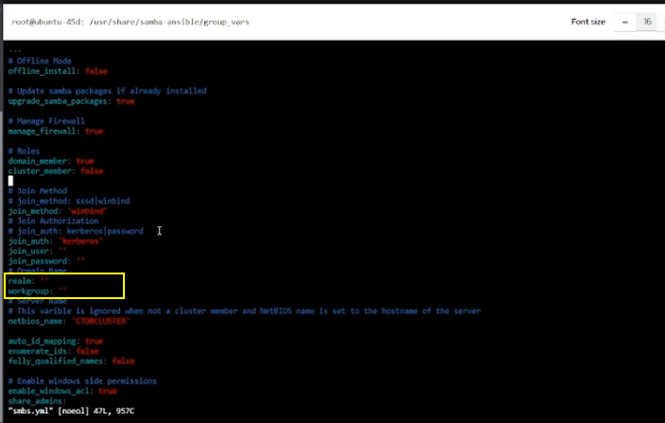
Open the smbs.yml file for editing and set the appropriate realm and workgroup for your Active Directory domain:
For example, if your domain is 45SUPPORT.LOCAL:
realm: ’45SUPPORT.LOCAL’
workgroup: ’45SUPPORT’
Step 2: Authentication and Running the Playbook
Generate a Kerberos ticket for the AD user and then execute the Samba-Ansible playbook to perform the domain join.
If using Kerberos authentication, generate a Kerberos ticket before running the playbook.
Replace user@REALM with your domain user principal:
kinit user@REALM
Example:
administrator@45SUPPORT.LOCAL
Verify that Ansible can connect and run commands on the server using the generated inventory file:
ansible -m ping all -i hosts
Navigate back to the main playbook directory:
cd /usr/share/samba-ansible
Run the domain join playbook. The smb.yml playbook handles the configuration and domain join using Winbind:
ansible-playbook -i hosts smb.yml
Upon successful execution, the domain has been joined.
Step 3: Verify Domain Users and Groups
Use the wbinfo utility to confirm that the system is successfully resolving users and groups from the Active Directory.
To verify domain users are resolvable:
wbinfo -u
To verify domain groups are resolvable:
wbinfo -g
The output should list the users and groups present in your Active Directory domain, confirming a successful domain join.
Troubleshooting
- Ensure you have configured the server hostname and DNS address correctly.
- Ensure you have configured nsswitch.conf correctly.